Auto insurance works by providing financial relief after damages and injuries involving your car. You have various coverage options, price points and companies to choose from.
Regardless of the company or type of car insurance you choose, each policy works in a similar way. You'll typically pay a monthly or annual premium for coverage. If you experience a covered incident, you can then file a claim for damages or injuries against your auto insurance policy, up to its limits.
Learn how car insurance works:
How does my auto insurance policy work?
Regardless of what type of car insurance you select, the nuts and bolts of each policy are pretty much the same. The main parts of an auto insurance policy you'll probably deal with are:
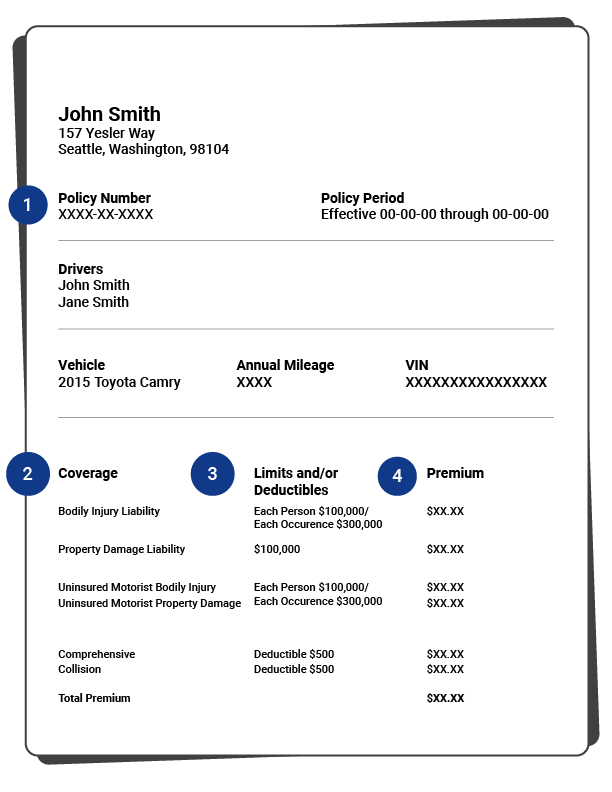
- Policy number: An identification number given when you sign up for a policy. Insurance companies will use this to identify your account. You will usually need this when contacting your insurer, getting involved in an accident and registering or buying a vehicle.
- Coverage: Each auto insurance policy type has specific perils that are expressly included and excluded in your coverage. Your policy coverage should be clearly listed. However, you should make sure to go over your coverage with your auto insurance company before you commit to a policy. Make sure you're not missing any coverage you need.
- Limit: Every type of auto insurance has a maximum amount it will payout on a claim. For example, say your liability coverage has a limit of $100,000 in bodily injury protection per person. If you hit someone with your car and the medical bill comes to $125,000, you're responsible for paying the remaining $25,000.
- Premium: This is the amount you pay in order to keep your car insurance policy active. Auto insurance providers usually require you to pay your premium monthly, bi-annually or annually.
You may also find a list of exclusions. Each auto insurance policy type has specific perils that are expressly not included in your coverage. Your policy exclusions should be clearly listed. However, you should make sure to go over your coverage with your auto insurance company before you commit to a policy. Make sure you're not missing any coverage you need.
What to know about car insurance
Bodily injury and property damage liability coverages
Two types of liability coverage are required in almost every state — bodily injury liability and property damage liability.
Liability insurance covers damage and injuries to others. It does not cover you, your passengers or your car. If you cause an accident that injures someone or damages their property, including their car, liability coverage helps to compensate them.
| Liability coverage | What does it cover? |
|---|---|
| Bodily injury | Medical and legal expenses, lost wages, funeral costs, pain and suffering. |
| Property damage | Court fees, damage to another person's car and property such as their vehicle, fence, house, mailbox or business. |
Personal injury protection
Also known as PIP, personal injury protection takes care of medical costs for you and passengers in your car after an accident. It also covers required rehabilitation therapy and lost wages. PIP is no-fault insurance — meaning it kicks in no matter who is at fault for an accident — that is either required or offered as optional coverage in 20 states.
PIP covers many types of expenses related to injury in an accident. Whether it’s a one-time hospital visit, ongoing care or an operation, personal injury protection takes care of you financially by making sure you don’t get stuck with costly medical bills after an accident.
Uninsured/underinsured motorist coverage
Uninsured/underinsured motorist (UM/UIM) coverage protects you if you get into a crash with a driver with insufficient or no auto insurance. Specifically, it can ensure that you don't pay a large sum out of pocket. It can be especially useful if you get hurt in a hit-and-run accident.
It is common for drivers to be underinsured, so UM/UIM coverage is a good option for many drivers, especially in states with low liability coverage minimums.
UM/UIM covers bodily injury, but not always property damage. Make sure to double-check which type of coverage is required in your state, and which you have.
Rental car reimbursement
Also known as loss-of-use (LOU) coverage, this type of auto insurance covers rental car costs while your vehicle is in the shop after you make an auto insurance claim.
Medical payments (MedPay)
Medical payments coverage is similar to personal injury protection, but it covers fewer expenses — only medical bills and funeral costs. MedPay does not cover lost wages or other non-medical expenses like PIP might. Nevertheless, it can be a valuable protection for you and your passengers, as it covers injuries regardless of fault.
Gap insurance
Gap insurance (“guaranteed auto protection”) protects you if you experience a total loss and owe more on your car than your insurance pays out. A total loss can mean your car is totaled in an accident or stolen. Gap insurance is only for people with an auto loan, as money is still owed on the car.
Choosing between minimum and full-coverage insurance
When choosing a policy, you may hear the terms minimum and full coverage.
Almost every state requires drivers to carry car insurance. This legal minimum insurance, also known as minimum coverage, typically offers liability insurance, which only covers damages and injuries you cause to others.
"Full coverage" isn't an actual type of car insurance. It's a term for a combination of coverages — comprehensive, collision and liability — that helps pay for your damages and injuries after a crash. Full coverage costs quite a bit more than minimum coverage since minimum coverage doesn't cover your injuries or damages.
Liability insurance
Average cost: $1,040 per year
It covers:
- Medical costs from auto-related injuries you cause to others.
- Repair or replacement of property you damage.
- Your court costs that occur due to litigation.
Full coverage
Average cost: $2,108 per year
It can include:
- Collision insurance to cover your own damages from a car crash.
- Comprehensive insurance that covers damage from something other than a collision.
- Other insurance, like personal injury protection and uninsured motorist coverage.
How much car insurance coverage do I need?
You need to have the minimum liability insurance required by your state. However, this may not be enough to protect all of your assets in the event of an auto accident. States do not update their required liability limits often, and they may not reflect the actual costs that can occur.
Because of this, we recommend increasing your liability limits if your budget allows for it. For example, $100,000 in bodily injury protection per accident tends to be a common minimum coverage in many states. This seems like a lot of money until you have to pay for an extended hospital stay or a long court case. Either of these events can tear through $100,000 quickly, leaving you to pay the rest out of pocket. If possible, increase your liability limits to the following:
- $100,000 in bodily injury coverage per person.
- $300,000 in bodily injury coverage per accident.
- $100,000 in property damage coverage.
While state law doesn't require collision or comprehensive insurance, your lender will probably require it if you finance your vehicle. This is so it can protect its investment. Your lender will let you know what limits it requires. Even if you buy your car on your own, full coverage can be an excellent investment if the car is new.
How do I buy auto insurance?
Once you know the coverage limits and budget range you need in a car insurance policy, it's time to start shopping around. One easy way to buy car insurance is to go online and compare quotes from different providers. You can also check out individual auto insurance companies and independent providers. The more options you explore to find your best auto insurance quote, the higher your odds of finding the best policy for you.
Compare rates from top car insurance companies
Basic auto insurance policies tend to have standard coverage options. This means you'll want to look at each provider's pricing, additional benefits and discounts. It's also a good idea to look at each insurer's customer satisfaction trends. Consumer review sites like J.D. Power, as well as other online review sites, provide great starting points for comparison.
What factors affect your auto insurance premium?
Your auto insurance premium will likely take the biggest bite out of your budget, so you should know how it's calculated. Full coverage auto insurance costs $2,108 a year, on average. This rate is affected by:
- Your personal driving and insurance records: Auto insurers work hard to mitigate their risks, and they reward drivers whom they perceive as less risky. The cleaner your driving record and the fewer insurance claims you have made in the past, the lower your premium typically is.
- Your deductible: The higher your deductible, the lower your annual premium usually costs. If you can afford a high deductible, it may save you a significant amount of money over the long term.
- Your coverage limits: If you raise your auto insurance coverage limits above the basic minimum limits offered, your premium will rise accordingly. For many types of auto insurance, the premium increase may be quite low in comparison to the increase in coverage. It's worthwhile to at least consider higher coverage amounts for your peace of mind.
- Your location: If your ZIP code has a high crime rate, a history of traffic accidents or extreme weather patterns, your auto insurance costs may be higher.
References:
QuoteWizard.com LLC has made every effort to ensure that the information on this site is correct, but we cannot guarantee that it is free of inaccuracies, errors, or omissions. All content and services provided on or through this site are provided "as is" and "as available" for use. QuoteWizard.com LLC makes no representations or warranties of any kind, express or implied, as to the operation of this site or to the information, content, materials, or products included on this site. You expressly agree that your use of this site is at your sole risk.